
How does GPS find positions?
The receiver calculates a 3D position by measuring the ranges to at least 4 satellites.

Figure 4.1: Positioning
For the range measurement the receiver needs the two carriers containing code:
C/A-Code with a lenght of 1 millisecond
P-Code with a lenght of 7 days per satellite
The receiver generates the same code as the satellite and calculates the time it took to receive the signal by synchronizing the signals.
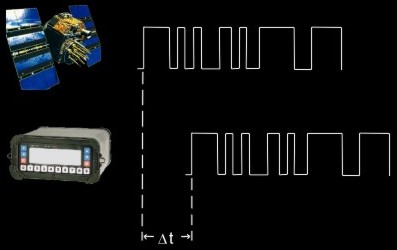
Figure 4.2: Determination of the time difference Dt
Range = Time Difference x Speed of Light
Auhtor: Michael Schulz, GEOSOFT